Proof of Work Explained Simply for Beginners


Proof of Work (PoW) is a cornerstone of blockchain technology famously at the heart of Bitcoin. PoW is a clever way for computers to show they’ve done a certain amount of work before adding new data like transactions to a shared digital ledger. This mechanism acts like a watchdog against fraud and keeps decentralized networks trustworthy without anyone playing the role of the big boss.
What Does Proof of Work Really Mean?
Proof of Work operates like a high-stakes race, where participants called miners scramble to crack tough mathematical puzzles. Think of it as a puzzle contest and the first one to crack it earns the honor of adding the next batch of transactions to the blockchain. This isn’t just for bragging rights—this whole process helps the network come to a solid agreement on the one true version of the data.
What Sparked the Creation of Proof of Work?
Proof of Work came along, digital currency systems were stuck facing some pretty tough hurdles—chief among them was figuring out how to stop people from spending the same digital money twice. Without a trusty middleman like a bank to keep things honest, it was a real challenge to verify who is playing fair. Proof of Work stepped in as a clever fix, making it both costly and tricky to mess with transaction records.
- Stopping double spending, which is what happens when someone tries to use the same digital coin more than once—kind of like trying to spend a single ticket twice at the movies.
- Functioning without relying on a central authority like banks or governments, so it’s more of a peer-to-peer party.
- Confirming transactions in a way that doesn’t require participants to put blind trust in each other—because trust can be tricky.
- Preventing fraudulent or fake transactions that could otherwise take a bite out of the currency’s value and leave everyone paying the price.
How Does Proof of Work Really Function A Closer Look
In a Proof of Work setup miners race against one another to solve tough cryptographic puzzles by endlessly guessing numbers called "nonces" until they find a hash that fits perfectly. The lucky miner who cracks the code first gets the honor of adding a fresh block of transactions to the blockchain and snagging a reward along the way.
Miners gather the freshest transactions that have not gotten their official thumbs-up yet and wait to add them.
They then bundle these transactions into a shiny new block.
Miners scramble to find a magical number called a 'nonce' that produces a hash meeting tough difficulty requirements when plugged in.
The lucky first miner to crack the code shouts out their victory by sharing the winning block with the network.
The other miners double-check that this block is legit before happily tacking it onto their copy of the blockchain.
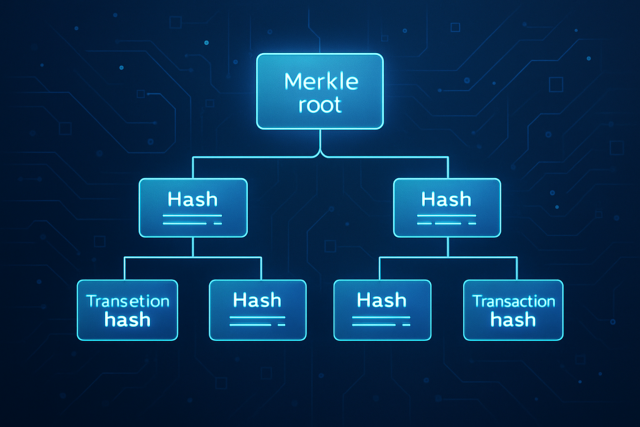
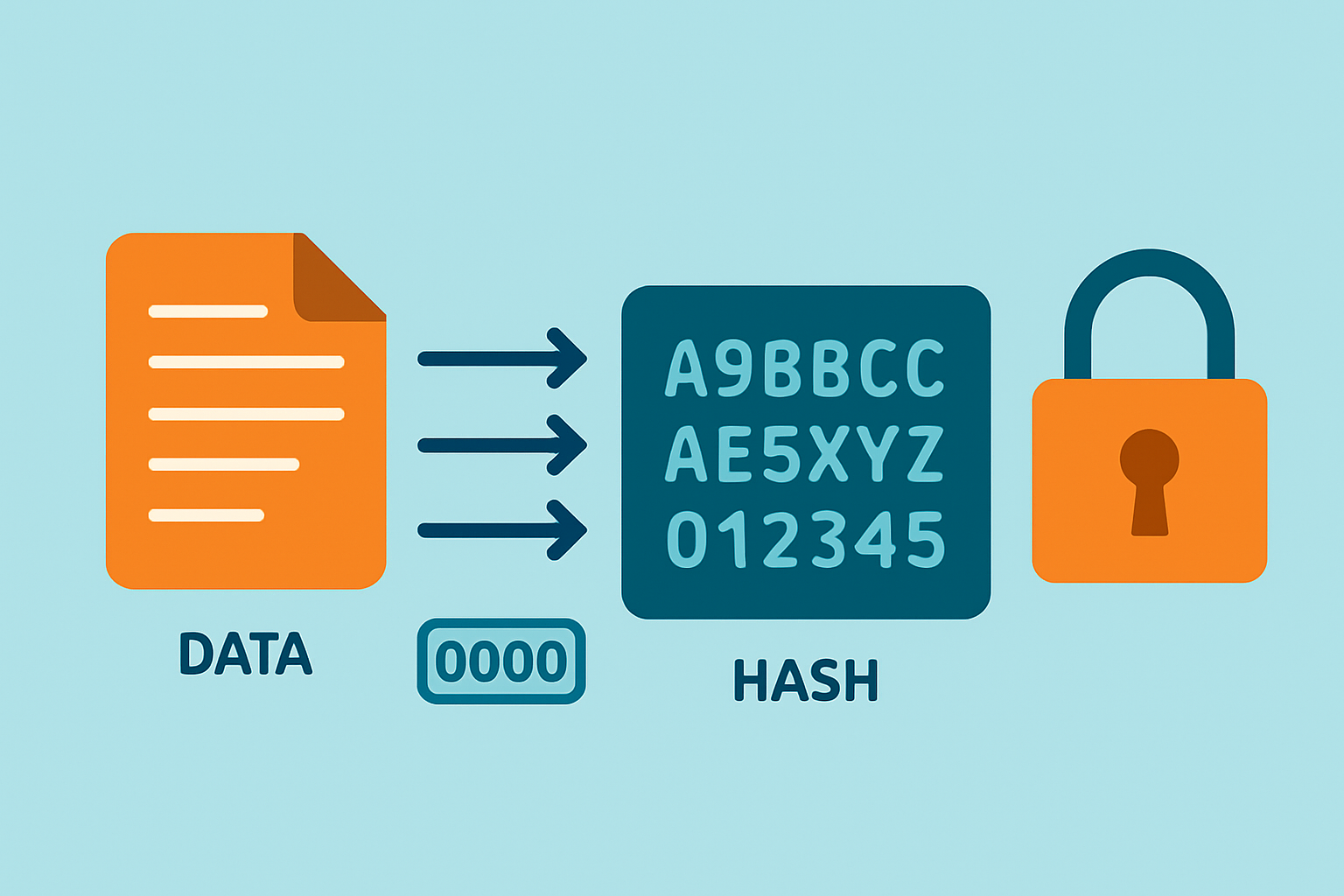
What a Hash Is and Why It Really Matters
A hash is essentially a unique string of characters with a fixed length crafted by running any input data—say transactions—through a cryptographic algorithm. Think of it as a digital fingerprint for that data. Even the tiniest change in the original input flips the hash and makes it nearly impossible to reverse-engineer or guess. When it comes to Proof of Work, miners are like detectives who tweak the nonce to hunt for a hash that starts with a specific number of zeros.
What Exactly Makes Proof of Work Feel Secure?
Proof of Work relies heavily on massive computing power and energy to crack its cryptographic puzzles. If someone wanted to tamper with any part of the blockchain, they’d have to redo this costly work for every block that comes after. Crucially, they must do it faster than the entire honest network combined. It’s a tall order.
Proof of Work is kind of like a super secure safe that demands a ton of effort to crack open. You really need to be willing to roll up your sleeves and invest a hefty chunk of time and energy to unlock it — which, in my experience, is exactly what keeps people from tampering with the blockchain.
Frequent Misunderstandings About Proof of Work What You Might Be Missing
- PoW doesn’t just burn through electricity without a purpose. The energy spent actually plays a important role in keeping transactions safe from fraud and attacks.
- Proof of Work isn’t the only way to reach consensus, but it is by far the most tried-and-true method that has stood the test of time.
- Mining isn’t a random guessing game. It follows strict cryptographic rules that leave very little room for chance.
- PoW networks aren’t inherently centralized, though mining pools often band together to boost efficiency and share the workload.
How Proof of Work Plays a Key Role in Locking Down Cryptocurrency Transactions
Proof of Work lets cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin securely confirm and validate transactions without needing a central authority. When you send Bitcoin, your transaction gets broadcast across the network and grabbed by miners who race to pack it into a block and confirm it once they crack the PoW puzzle.
A user kicks off a cryptocurrency transaction and sends it across the network for all to see.
Miners scoop up this fresh transaction and toss it into a growing pool of pending ones waiting in line.
Next, miners roll up their sleeves to crack the Proof of Work puzzle. They aim to slot a brand-new block loaded with these transactions onto the chain.
Once a miner nails a valid solution, they shout it out loud by broadcasting the new block to the entire network.
The other nodes don their detective hats and scrutinize the block before adding it to their versions of the blockchain, giving the transactions the official thumbs up.
Challenges and Critiques of Proof of Work
Navigating the world of Proof of Work is no walk in the park; it is more like a rollercoaster ride with its fair share of ups and downs. While it is the backbone of many cryptocurrencies, this mechanism does raise a few eyebrows due to its significant energy appetite and sometimes questionable scalability. Sure, it is proven resilient and pretty secure over the years, but let us be honest—it's not without its quirks and critics. From environmental concerns to the ever-looming threat of centralization, the challenges pile up faster than you would expect. Still, the conversation around Proof of Work keeps evolving, fueled by passionate debate and an ongoing quest for better solutions.
Proof of Work is a tried-and-true method that’s proven its reliability over time but often catches flak for guzzling electricity like there’s no tomorrow. This brings obvious environmental worries into the spotlight. On top of that it requires pricey specialized hardware to stay in the game which can throw a wrench into speedy transaction processing and broad scalability.
- PoW gobbles up a massive amount of electricity, which definitely doesn’t do its environmental reputation any favors.
- Mining requires some pretty specialized and pricey hardware, so it’s not exactly a level playing field for everyone hoping to turn a profit.
- Transactions can drag along at a slower pace compared to some other systems out there.
- Mining pools often end up hoarding control, which understandably stirs up concerns about the network tipping towards centralization.
Exploring Alternatives to Proof of Work
Other consensus methods like Proof of Stake (PoS) offer a neat alternative to Proof of Work by picking validators based on how much skin they have in the game rather than just brute computational muscle. PoS usually sips energy instead of guzzling it and can zoom through transactions faster, though it comes with trade-offs when you dig into decentralization and security.
| Consensus Mechanism | Energy Usage | Security Model | Transaction Speed | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Very High | Security depends heavily on computational muscle and hefty energy bills | Slower (takes minutes per block, so patience is a virtue) | Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum (before the merge) |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Low | Security is backed by economic skin in the game and penalties for misbehavior | Faster (measured in seconds to minutes, which feels like lightning compared to PoW) | Ethereum (after the merge), Cardano, Solana |
| Delegated PoS | Low | Validators get picked by delegation stakes, giving a bit of a popularity contest vibe | Very Fast (blink and you will miss it) | EOS, Tron |
| Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) | Moderate | Consensus happens when the majority of known validators raise their hands in agreement | Very Fast | Hyperledger Fabric, Ripple |
Why Proof of Work Still Holds Its Ground Today
Proof of Work still holds a starring role in securing some of the world’s largest and most valuable blockchains. Its resilience against attacks has stood the test of time for more than a decade now. Developers are always on the lookout for clever ways to make PoW leaner and greener, whether that means tapping into renewable energy sources or giving mining hardware a well-deserved upgrade.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does Proof of Work require so much energy?
Proof of Work uses a lot of energy because miners race to crack tough cryptographic puzzles. This demands massive computational power. The high energy cost helps keep the system secure by making attacks expensive. It’s a trade-off that deters fraudsters and maintains trust in decentralized networks like Bitcoin.
Can Proof of Work be hacked or manipulated?
Messing with Proof of Work is very difficult since an attacker must control over 51% of the network’s mining power to rewrite transactions. Given the huge costs and effort, attacking big blockchains like Bitcoin is practically impossible. Overall, PoW is very secure against tampering.
What happens if no one mines in a Proof of Work system?
If miners stopped, the network would stall because new blocks would not be added. Fortunately, mining rewards motivate miners to keep working for those rewards and transaction fees. This competition keeps the blockchain running and secure in practice.
Is Proof of Work the only way to secure a blockchain?
Not at all. Other methods like Proof of Stake use validators instead of miners and offer a different approach to security. However, PoW remains the proven method, especially for major blockchains like Bitcoin. Some newer blockchains combine approaches or use PoS to reduce energy use while maintaining safety.
How long does it take to mine a block in Proof of Work?
For Bitcoin, the target is about 10 minutes per block. The system automatically adjusts difficulty as miners join or leave to keep block times steady. Other PoW blockchains may have different targets based on their design.
Can I participate in Proof of Work mining at home?
You can try, but solo mining on a regular computer usually is not profitable because of fierce competition and specialized hardware like ASICs. Most miners join pools to combine resources and share rewards. Your income depends heavily on electricity costs and your equipment’s efficiency.